Blood cancer is a chronic disease that is also named “hematologic cancer.” This cancer starts in blood-forming tissues such as bone marrow or the lymphatic system. This type of cancer interferes with the production and function of blood cells. Its symptoms and treatments depend upon the type of blood cancer and the characteristics of the disease. This is a dreadful disease that costs several lives annually, but early detection and improved medical treatments proved helpful in reducing the number of causalities. This article will provide readers with detailed knowledge about blood cancer, its history, types, causes, symptoms, and remedies. First of all, have a look at the history of blood cancer.
The history of blood cancer dates back centuries with the evolution of different treatments and understanding with time. Detail is given as follows:
- Early Observations: Blood cancer has existed for several centuries, but different types were not differentiated at that time. In historical texts, symptoms of blood cancer include enlarged lymph nodes and weakness; today, that is known as leukemia or lymphoma.
- Advances in Understanding: The 19th century marks a significant development in the history of blood cancer. In 1845, Rudolf Virchow introduced the term “leukemia,” described from the Greek word “white blood. This term describes the disease with the overabundance of white blood cells in affected individuals. From here, leukemia is differentiated from other types of blood cancer.
- Treatment Evolution: The 20th century marks the development of the treatments and remedies for blood cancer. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy were introduced in this era. Chemotherapy proves remarkable not only for blood cancer but for other types of cancer as well.
- Advances in Transplantation: At the end of the 20th century, a technique for stem cell transplantation was introduced to cure some potential types of blood cancer. In this procedure, diseased or damaged bone marrow is replaced with healthy stem cells that lead to the formation of normal blood cells.
- Targeted Therapies and Immunotherapy: Advancements in recent decades have witnessed the introduction of targeted therapies and immunotherapy that target cancer cells with less damage to normal cells. These treatments improve patients’ quality of life.
Moreover, research continued to improve technological advancements and clinical trials so that with more scientific discoveries, treatments may be improved.
Types of Blood Cancer:
Major types of blood cancer are given as follows:
- Leukemia: In this type of blood cancer, the body produces white blood cells in overabundance that cannot fight infections. Leukemia is divided into four types, which are given as follows:
- Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL): This type of leukemia is common in childhood.
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML): This type of leukemia is mostly common in people over the age of 65.
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): This type of leukemia is most common in adults.
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML): This type of leukemia mostly affects adults, but children can also be affected by it.
- Lymphoma: This type of blood cancer affects the lymph system, which includes the lymph nodes, spleen, and thymus gland. Two major types of lymphoma are given as follows:
- Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
- Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
- Myeloma: This type of blood cancer affects the plasma cells in the bone marrow, which make antibodies. This cancer is usually known as multiple myeloma.
- Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS) are a group of disorders caused by dysfunctional blood cells in the bone marrow.
- Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MPN): In this type of disease, blood cells grow abnormally in the bone marrow.
Causes of Blood Cancer:
Several factors contribute to the development of bone cancer. Major causes of blood cancer are given as follows:
- Genetic Factors: Genetic factors include genetic mutations and inherited genetic syndromes. Some genetic mutations lead to the development of blood cancer. Such genetic mutations are:
- The Philadelphia chromosome in chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML)
- Mutations in genes like TP53, FLT3 and NPM1in acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
- Mutations in genes such as BCL2, MYC, and others in different types of lymphoma
Some inherited genetic syndromes, such as Down syndrome and Li-Fraumeni Syndrome, cause blood cancer to develop.
- Environmental and Lifestyle Factors: Some environmental and lifestyle factors that cause blood cancer are given as follows:
- Those who are exposed to high-level radiation (for the treatment of disease, atomic bomb radiation) are more at risk of blood cancer.
- People exposed to certain chemicals, such as benzene, pesticides, and chemotherapy, may also be affected by the disease.
- Moreover, different viruses, such as Epstein-Barr virus and the Human T-cell lymphotropic virus, may also lead to the development of blood cancer.
- Other risk factors such as age and gender also have a link with blood cancer. As mentioned above, some types of leukemia are common in children, while others are in both adults and children. Likewise, some types of cancer are more common in one gender over the other, such as Hodgkin Lymphoma, which is more common in males than females.
Symptoms of Blood Cancer:
Symptoms of blood cancer are given as follows:
- Anemia is when the body does not make enough red blood cells. It includes:
- Tiredness and weakness
- Difficulty in breathing
- Dizziness
- Pale Skin
- Chest pain
- Poor Clotting: A condition in which platelets in your body do not make enough clots. It includes:
- Bleeding gums
- Tiny red dots on your skin
- Unusual bruising
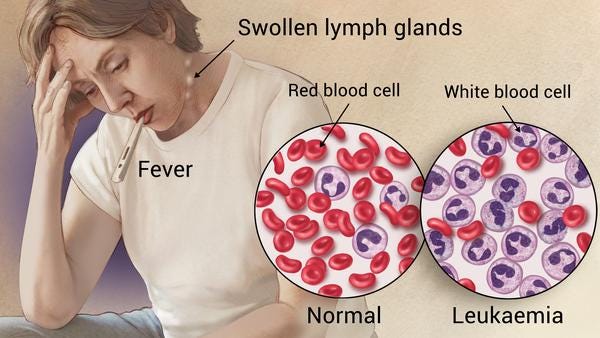
- Leukemia: This condition relates to the formation of abnormal white blood cells. Its symptoms are:
- Fever or chills
- Constant fatigue or weakness
- Severe infections
- Weight loss
- Swelling in lymph nodes, enlarged liver
- Easy bleeding
- Bone pain
- Excessive sweating
- Lymphoma: Lymphocytes go out of control.
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Fever
- Tiredness
- Itchy skin
- Multiple Myeloma: Bone marrow makes plasma cells abnormally.
- Bone pain
- Hypercalcemia: High level of calcium in your blood.
- Nausea and stomach pain
- Constipation
- Excessive thirst and urination
Remedies for Blood Cancer:
Remedies for blood cancer are given as follows:
- Chemotherapy: Use of drugs to stop cancer or kill cancer cells.
- Radiation Therapy: In this remedy, high-energy radiations kill cancerous cells.
- Targeted Therapy: Target cancer cells destroyed by the use of drugs.
- Immunotherapy: This therapy strengthens the immune system to fight the disease.
- Stem Cell Transplant: This remedy replaces damaged bone marrow with healthy stem cells.
- Precision Medicine: Tailors treatment to individual genetic profiles.
- CAR-T Cell Therapy: Modified T cells are used in this therapy.
- Supportive Care: Handle symptoms and side effects.
- Clinical Trials: Investigates new treatments and therapies.
Integrative Therapies:
Integrative therapies can also be used as a remedy for blood cancer, but they cannot be used as an alternative to medical treatment. One must be in contact with healthcare professionals while using these therapies. Some integrative therapies are given as follows:
- Acupuncture
- Massage
- Meditation
- Yoga
- Healthy Diet
- Herbal remedies (turmeric, ginger)