Brain cancer is a chronic disease that has been at the top of the list of medical researchers for decades. This article would provide its readers with the details of the chronic disease that has been the cause of several deaths every day all over the world. Let’s have a look at the introduction of “brain cancer”.
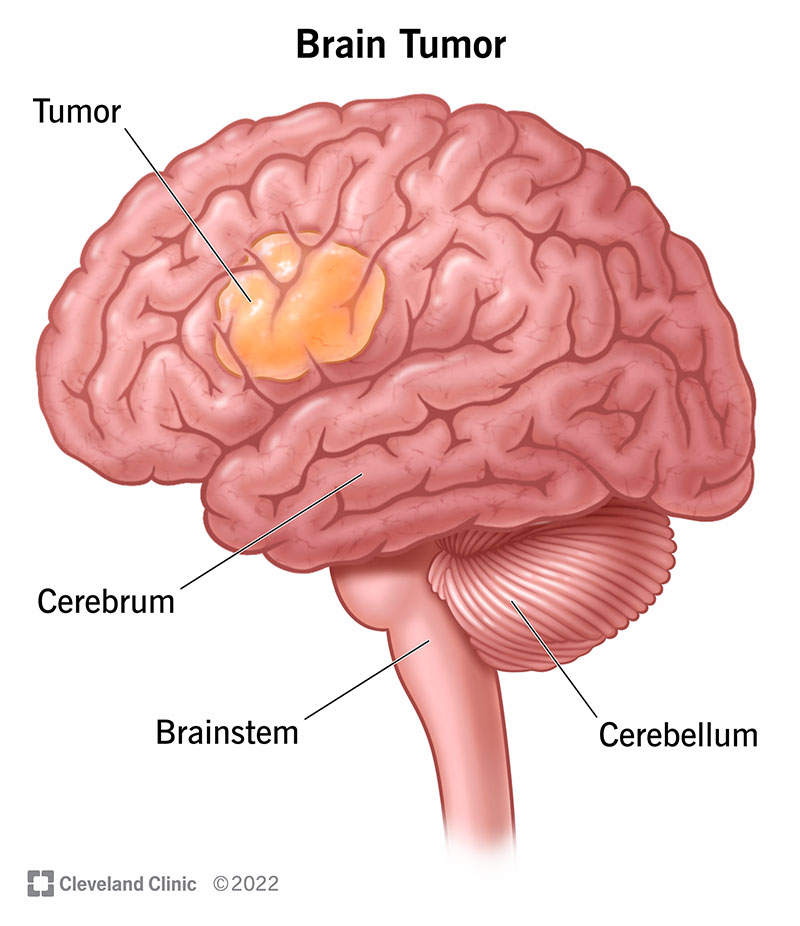
The brain is the body’s main organ with the cerebrum, cerebellum, and four lobes. Normal functioning of the body depends on the normal functioning of the brain. Any malfunction in the brain’s anatomical structure and unusual growth of cells within the brain tissues affects the brain’s normal functioning. The first recorded mention of a brain tumor dates back to 1600 BCE. In the 5th century BCE, the Greek physician describes the case of a woman with a brain tumor. In the 18th and 19th centuries, many researchers studied the brain cancer. At the start of the 20th century, various advancements were made related to brain cancer including brain tumor surgeries performed by neurosurgeons. In the middle of the twentieth century, more advancements were made in the field of brain tumors such as CT and MRI scans. Moreover, advances in understanding brain tumor genetics and molecular biology have led to targeted therapies and personalized medical approaches.
Brain tumors can develop from brain cells and also from other parts of the body to the brain. This abnormal growth of cells can be benign and malignant. Benign tumors are noncancerous. They grow slowly and do not spread to the other parts of the body. They do not grow to nearby tissues, have boundaries, and may not require medical treatment. On the other hand, malignant tumors are cancerous, they proliferate and spread to the different parts of the body. This type of brain cancer may activate again after its removal, severely disturb the normal functioning of the body, and require aggressive treatment. Some other types of brain cancer are given as follows:
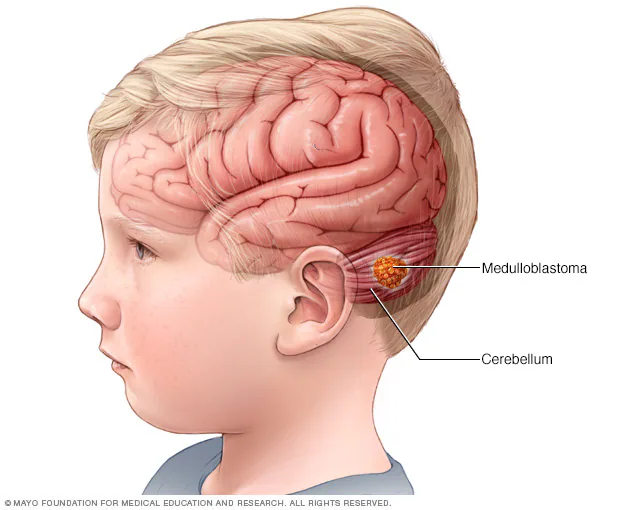
Glioblastoma: This type of cancer forms in the cells that support nerve cells.- Medulloblastoma: This type of cancer forms in the part of the brain i.e. cerebellum.
- Acoustic Neuroma: This type of tumor is non-cancerous and it develops in the nerves of hearing and balance.
- Gliomas: These types of cells are similar to glial cells.
- Choroid Plexus Tumors: This type of tumor is in the cells that make cerebrospinal fluid.
- Nerve Tumors: This type of tumor is caused by the cells that develop in and around the nerves.
- Meningiomas: This type of tumor develops around the membranes of the spinal cord and brain.
- Pineal Tumors: A tumor that develops around the pineal gland is known as a pineal tumor.
Major Causes of Brain Cancer:
Some major causes of brain cancer are as follows:
Radiation Exposure: Radiations from radiation therapies, X-rays, and CT scans increase the chance of brain cancer.- Infection: Some particular infections like the Epstein-Barr virus that cause mononucleosis increase the possibility of brain cancer.
- Workplace Exposure: Interaction with different chemicals and pesticides at the workplace also increases the possibility of brain cancer.
- Smoking: A person with a long-term smoking habit is more at risk of brain cancer.
- Gene Changes: Alteration in genes that control cell growth and division also increases the danger of brain cancer.
- Age: There is no specific age for being affected by cancer. It can start at any age. But as age increases the risk of brain cancer also increases. The risk is greatest at the age between 85 and 89 years.
- Overweight and Obesity: Obesity is a disease itself. Being overweight exaggerates the situation and increases the risk of different types of cancers, and one of them is brain cancer. Meningioma is a type of brain tumor that is caused by overweight and obesity. Every year about 2 percent of patients with brain tumors have a cause of obesity.
- Family History and Genetic Conditions: The risk of this type of cancer is higher in families who already have a patient with a brain tumor i.e. parents, siblings, or child. Brain tumors are also due to genetic conditions. Some syndromes increase the risk of brain cancer. The names of syndromes are as follows:
Neurofibromatosis (NF) type 1 and type 2- Tuberous sclerosis (TSC)
- Li-Fraumeni syndrome
- Vo Hippel-Lindau syndrome (VHL)
- Turner syndrome
- Turcot syndrome
- Gorlin syndrome
Major Symptoms of Brain Cancer:
Some common symptoms of brain cancer are as follows:
Headaches- Nausea and Vomiting
- Balance and Coordination Issues
- Memory Lapses
- Difficulty in Thinking and Speaking
- Vision Problems
- Personality Changes
- Seizures
- Drowsiness
- Numbness or Tingling in Arms and Legs
- Muscles Jerking or Twitching
- Weight Gain and Increased Appetite
- Difficulty in Walking and Maintaining Balance
- Hearing Problems
- Vertigo or Dizziness
Remedies for Brain Cancer:
Surgery: Surgery is used for the treatment of many types of brain cancers. The purpose is the removal of tumors from the brain as much as possible without damaging the tissues of the brain.- Radiation Therapy: In this type of remedy, high-energy radiation is used to destroy the cancerous cells. Radiations can be provided from outside the body or with the help of a device placed inside the body near the tumor.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy refers to the use of drugs to destroy brain cells. The intake of these drugs is orally or intravenously, it reaches the cancerous cells of the brain by passing through the bloodstream.
- Targeted Therapy: In this kind of therapy, drugs target the specific abnormalities in brain cells.
- Immunotherapy: This therapy makes the immune system stronger to recognize and fight the disease.
- Rehabilitation Therapy: This includes physical, occupational, and speech therapies to help recover lost abilities. It is an important part of the treatment.
Supportive Care:
There are no proven home care remedies for the treatment of brain cancer but they can be taken along the medical treatments for the speedy recovery from the disease. Supportive care can be used as an extra treatment but not an alternative to proper medical treatment. Some of these supportive care treatments are as follows:
Mind-body Therapies: Meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises.- Dietary Changes: Increases the intake of fruits, vegetables, nuts (antioxidants), Omega-3 fatty acids (salmon, walnuts), and curcumin.
- Herbal Supplements: It includes Green Tea extract, Ginger, and Ashwagandha.
- Vitamins and Minerals: It includes Vitamin D, Vitamin K, and Magnesium.
Other supportive care therapies include Acupuncture, Massage therapy, Aromatherapy, Music therapy, Art therapy, exercise, and physical activity. However, the patient must be careful and consult the doctor for professional guidance while using these therapies.